internal medicine
Internal Medicine Clinic

01
What is diabetes?
Most of food we eat is used as energy sources after going through the process of breaking down into glucose and moving into the blood vessels. During this process, insulin, the hormone secreted form pancreas, act a role of sending glucose into cells. When insulin is not produced or cells don't react to insulin, produced glucose cannot go into cells but stay in the blood, resulting in increasing blood sugar. This condition is called diabetes.
02
What cause diabetes?
-
Genetic factor It is closely related to family history, and recent statistics show that when both parents are diabetic, the chance of developing diabetes for the child is 58%, and when one parent is diabetic, the chance is 28%.
-
Environmental factor ㆍEating high-calorie foods often
ㆍObesity due to less activity than food intake
ㆍAcute stress
ㆍLong-term use of adrenal cortical hormone or oral contraceptives
ㆍAging -
Immunological factor When autoimmune disease develops, it may lead to diabetes, and this is common in type 1 diabetes.
03
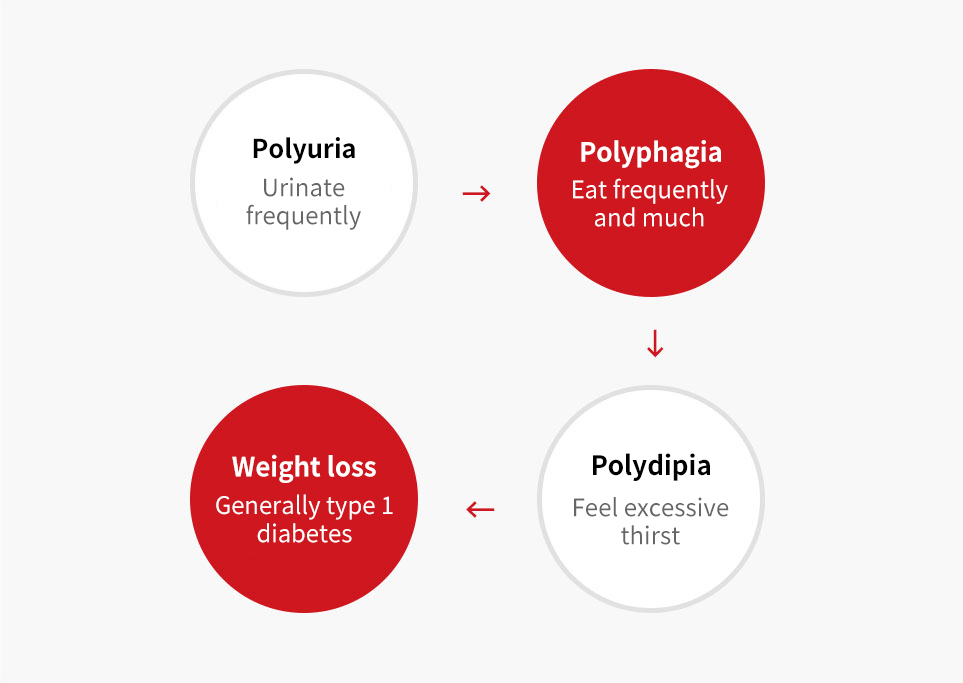
Weight drops, frequently urinate, eat more, and drink more water... what does it mean?
Since symptoms of diabetes vary and some cases show no symptoms, 20% of diabetes patients are detected during regular health checkups or some are diagnosed when they see a doctor due to symptoms of complications.


04
Most adult cases, type 2 diabetes
05
Subjects for regular checkup
Since diabetes are diagnosed by chance in many cases, no symptoms do not mean no diabetes. If more that one of the followings are applicable, regular checkup for diabetes is needed.
06
How to diagnose diabetes?
| Diagnostic criteria of diabetes | normal | Disturbed glucose tolerance | Diabetes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fasting blood sugar after 8 hours fasting | under 100lmg/dl | 100~125mg/dl | over 126mg/dl |
| Oral glucose tolerance test (blood sugar 2 hours after taking glucose solution) |
under 140mg/dl | 140~199mg/dl | over 200 mg/dl |
* Diagnostic criteria of diabetes(75% oral glucose tolerance): vein serum blood sugar
Perform blood test. In the case of no symptoms, when blood sugar level after 8-hour fasting is over 126mg/dl or blood sugar level 2 hours after taking glucose solution is over 200mg/dl is diagnosed with diabetes. And iit is also diagnosed with diabetes when drink a lot of water, urinate more, lose weight, and blood sugar level (random sugar test) measured regardless of meal intake is over 200mg/dl.

07
Diabetes treatment with dietary
therapy and exercise therapy
Dietary control and regular exercise are needed base on the medication when sugar in unmanageable. The primary goal of diabetes treatment is to maintain normal body weight and relieve symptoms in order to enable normal social activities. And the next goal is to prevent diabetes complications or delay their progression as much as possible.
Blood sugar check before exercise
It is possible to exercise safely when blood sugar level is in between 100-250mg/dl.
| Blood sugar level | Exercise or not |
|---|---|
| Under 70mg/dl & symptoms of hypoglycemia | Do not exercise |
| 80-100mg/dl | Possible after eating snacks |
| Over 250mg/dl & keton in urine | Do not exercise |
| Over 300mg/dl | Do not exercise |
Blood sugar check after exercise
When postexercise blood sugar level is under 100mg/dl and there are symptoms of hypoglycemia, take glucose as much as of 3 candies or half a glass of juice. Blood sugar level changes which have been checked before and after exercise can be a reference for the future exercise plan. When there are complications: If there are complications, consult with a doctor beforehand.
-
Retinopathies Prohibit breath holding exercise, high intensity exercise
Prohibit exercise with head down and shaking
Prohitbit excessivey heavy load muscle exercise -
Autonomic disturbance Prohibit exercise when heart rate increses at rest and maximum heart rate decreases
Be careful for dehydration and hypothermia
Observe blood sugar level change carefully
Avoid extreme workout environment -

Peripheral nerve disorder Caution for foot trauma
Put on well-fitted shoes
Prohibit excessive balance exxercise
Prohibit swimming when have ulcers -

Kidney disease Prohibit breath-holding exercise, heavy load muscle exercise
Be careful for dehyration -

Hypertension Prohibit breath-holding or heavy load muscle exercise
Medicinal therapy
-
Oral hypoglycemic agent It is mainly prescribed for Type 2 diabetes patients who are difficult to be cured only with dietary therapy.
The medications are sulfonylurea and biguanide. -
Insulin injection therapy Insulin is classified into 3 types depending on the speed of action in the body; fast-acting, regular, protracted.
The fundamental effect is same, that is reducing blood sugar level. But 'when become effective after injection', 'when the biggest effect comes' and 'how long the effect lasts' are different by types.
A combination of a fast-acting and a regular can be available for patients who have difficulty managing blood sugar level. -
Runnning 24 hours, insulin pump Insulin pump is a device which let insulin be administered into the body 24 hours.
It continuously injects small amount of fast-acting insulin, adjusting doses of insulin accordingly to meals.



