internal medicine
Internal Medicine Clinic
01
What is hyperlipidemia?
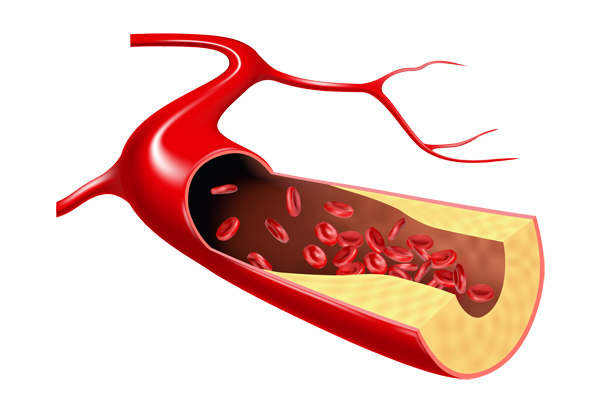
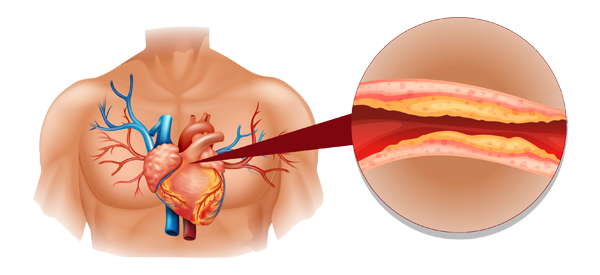
Cholesterol, which forms cell membrane and is needed to maintain life by becoming base material for steroid hormones, is a essential substance for the human body, but when excessive, it accumulates on the lining inside of the vessels, causing arteriosclerosis. Various substances such as cholesterol, calcium, etc. accumulate on the inner wall of damaged blood vessel, and these substances make wall of blood vessel hypertrophic by multiplying cells, eventually, wall of blood vessel is gradually narrowed. This is called atherosclerosis. These plaque parts are unstable, prone to rupture, and concurrently, cause local blood clotting, resulting in complete blocking of the vessel. When the coronary arteries which supply blood to the heart are blocked, it causes myocardial infarction, and when the cerebral blood vessels are blocked, it causes stroke.
02
Let's understand about cholesterol!
Blood lipids include cholesterol, cholesterol esters, phospholipids, triglycerides, fatty acids, etc., and as lipids absorbed into the blood do not dissolves in water, they are moved surrounded by proteins. This combination of fat and protein is called lipoprotein. This combination of fat and protein is called lipoprotein. Depending on its density, lipoprotein is classified chylomicron(CM), very low-density lipoprotein(VLDL), intermediate-density lipoprotein(IDL), low-density lipoprotein(LDL), and high-density lipoprotein(HDL).

03
Absorption, discharge, accumulation
of cholesterol
Cholesterol is synthesized in the liver(about 1,000mg daily) or comes into the body through food intake(about 400~500mg), and the main route is intake of animal foods(meat, fish, poultry, dairy products, egg yolks, etc.). Cholesterol and lipids in foods are digestedd and absorbed in the intestines, and travels from intestinal wall into the blood in a form of chylomicron(CM). Triglycerides are broken down and released by reacting with steatolytic enzymebreakdown enzymes in the blood, and there is relatively much cholesterol remains in the residues of chylomicron(CM), And these residues are absorbed into the liver.
04
Function of liver
The liver synthesizes very low-density lipoprotein(VLDL) and releases it into the blood. Like chylomicron(CM), the residues of very low-density lipoprotein(VLDL) which is remaining after the breakdown of triglycerides is called intermediate-density lipoprotein(IDL), and they are also absorbed into the liver, or some of them are converted to low-density lipoprotein(LDL).


05
Hyperlipidemia needs
“Every day management”
Low density lipoprotein(LDL) is a blood cholesterol carrier which mainly contains cholesterol. Some are used to make cells in tissues, and some are absorbed into the liver. However, as mention at first, when too much of LDL cholesterol is circulated into the blood, it accumulates on the inner wall of the blood vessels, reacts with various substances, and causes atherosclerosis by forming plaque. That is why LDL cholesterol is called bad cholesterol. When it increseases more than 160mg/dL, the risk of cardiovascular system increases. When having a history of cardiovascular disease or having diabetes, it is recommended to maintain LDL cholresterol level less than 100mg/dL.



