cancer clinic
Cancer Immunity Clinic

01
Definition
Brain tumor, i.e. intracranial tumor is a generic term for primary intracranial tumor, which develops in the brain tissue or membranes surrounding the brain, and secondary intracranial tumor which is metastasized from the cranium, its surrounding frames, or the distant part from the brain, and it includes neuroglioma, astrocytoma, malignant astrocytoma, glioblastoma, meningioma, pituitary adenoma, jneurinoma, congenital tumor, metastatic brain tumor, etc.
02
Characteristics
Intracranial tumor shows some distinctive aspects compared to other cancers developed in other organs. Since tumor develops inside the cranium which is very hard, neurological symptoms may appear at early stages as tumor grows, and symptoms for increased intracranial pressure are shown. In many cases, tumors may considered as malignant because, depending on the developed location, its complete removal is impossible even though it is histologically benign. Blocked stream of cerebrospinal fluid by tumor may cause hydrocephalus, and it is very rare that tumor metastasizes outward of the central nervous system.
03
Symptoms
Symptoms varied depending on types of tumor cells, growth speed, and developed location of tumor
Clinical symptoms of brain tumor is highly affected by physical reaction over the brain pressure increase and immune reaction as well as types of tumor cells, growth speed, and the location where tumor has developed in the cranial cavity.
04
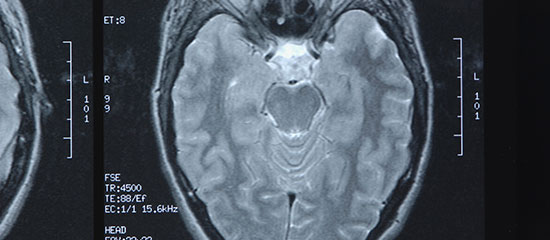
Diagnosis
Neuroangiography
05
Treatments
For brain tumor treatment, surgery, radiotherapy, anti-cancer chemotherapy, etc. are used
. Brain tumor treatments include surgical removing operation, gamma knife treatment which is a non-invasive treatment using gamma rays, irradiation therapy, and chemotherapy which uses anti-cancer medications, and these treatments may be used individually or in combination.
06
Management after treatment
As the follow-up examination after treatment, patients can be regularly monitored whether there is any signs of recurrence by undergoing MRI and CT.
The follow-up examination is performed once in 3 to 6 months depending on the type of tumor and a doctor.



