cancer clinic
Cancer Immunity Clinic
01
Definition of Cancer
Our body is made up of about 10 trillion cells. Some of these cells mutate, and proliferate uncontrollably and infinitely as long as they receive nourishment. Then they start comppressing surrounding organs, infiltrate into the nearby tissues and/or organs, and eventually disrupt their functions. These cells are called malignant tumors, that is cancers
Normal cells have both oncogenes that promote cancer growth and anti-oncogenes that inhibit cancer growth. Those two types of genes control mutually, so that the cells can be normal. However, involving loss of these control due to the carcinogen from external environment and/or other factors, cancerization appears in one cell or multiple cells through various complex stages for the period of several years or tens of years .
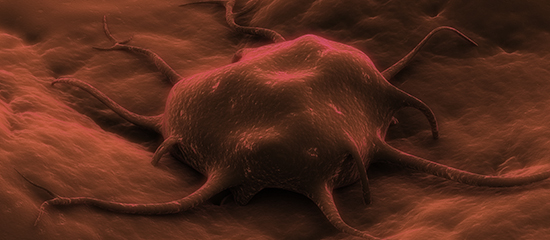
02
Characteristics of Cancer
- 01
Cancer infiltrates
- 02
Cancer metastasizes
- 03
Cancer sows the seeds
- 04
Cancer easily bleeds
- 05
Biochemical characteristics of cancer
Cancer shows symptoms of decrease of appetite, anemia, pains, high fever, edema, etc. The status characterized by those symptoms is called cancer cachexia. Tumors secrete cytokines, autocrines, paracrines, endocrine substances, etc., which occur febrility, cancer cachexia, leukocytosis, etc. For human cells' metabolism, cancer cachexia can be described as a wasting status which expresses loss of body weight, disorders in intake, absorption, use of nutrition
03
Risk factors for Cancer
- Persons with hight levels of estrogen may be put at a high risk of caners.
· Cigarette smoking is the No. 1 risk factor for cancers.- Cancer is not a hereditary disease. Proto-oncogenes are normal genes, however
when they are activated by various risk factors, they may result in cancerization.
- Some cases of breast cancer, ovarian cancer, colorectal cancer, etc., may caused by genetic factors.
· Race, ethnicity, etc. may act as internal factors. · Mental stress is the main culprit of cancer.04
Prevention of Cancer

Primary Prevention

Secondary PreventionEarly diagnosis &
early prevention
Tertiary PreventionRehabilitation after treatment &
Recurrence Prevention
05
How to Prevent
06
Cancer-causing Gene, Oncogene
An oncogene is a gene that has a certain role in a normal cell but accelerates the cell grow uncontrollably when mutated.
- 01
Cell Proliferation Factor
- 02
Cell proliferation Factor Receptor
- 03
Signal Transduction Factor
- 04
Tumor Suppressor Gene
When there are mutations in those four above, they make oncogenes.
In human cancers, there are four, high frequency reasons of cancer occurrences as follows:
1)Mutations in RAS gene family - RSA gene family is a family of genes that has an important role in signaling pathways. Mutated forms of RAS gene is the mostly found in human cancers. 2)Amplification of ErbB gene family - ErbB-1 and ErbB-2 express more about 30~40% in breast cancer, ovarian cancer, gastric cancer, bladder cancer etc., and 20~30% of them show amplification of genes. Expecially, when ErbB-2 excessively expresses, prognosis is poor.3)RET gene - Mutated forms of RET genes cause FMTC(Familial Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma), papillary thyroid cancer, the most common form of thyroid caner, and hirschsprung's disease (congenital aganglionic megacolon) which causes abnormalities in enteric nervous system.4)Activation of MYC gene family by chromosomal translocation - In case of burkitt lymphoma, when infected by EBV(Epstein-Barr Virus), leukemia develops by abnormalities of c-Myc gene expression. N-Myc, L-Myc, etc. are in the same family of c-Myc, they respectively proliferate in neuroblastoma, small cell lung cancer, etc. The probability of error occurrence as cells divide is just one forth.
Conclusion : In human body, there is a mechanism which recover damaged genes. However, when this mechanism cannot act properly due to genetic deficiency, etc. cell proliferate abnormally.
07
Diagnosis of Cancer
Target cancers for early diagnosis for Korean
Gastric cancer, Liver cancer, Breast cancer, Colon cancer, Cervical cancer, Thyroid cancer, Lung cancer, Esophageal cancer, Bladder cancer
| Type of Cancer | Examination Method | Advantages of Examinination | Disadvantages of Examination |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gastric cancer | Endoscopy | Accurate diagnosis, biopsy, and brief treatment are possible | Patients may feel sick and difficulty |
| Upper gastrointestinography | It is relatively easy to get.The entire shape of tumors can be seen.It is useful to plan for treatment | It is less accurate. Biopsy is impossible. | |
| Liver cancer | AFP(Alpha-fetoprotein) test | It is simple and cheap. | It is less accurate. |
| HepaCheck | It is simple. | Accuracy is high.(92~96%) | |
| Liver ultrasonography | It is a painless non-invasive test with accuracy. | Results may be different depend on operator's skill and related knowledge. | |
| Breast cancer | Mammography | Recently released digital devices are favorable for checking overall shape and detecting lesion, and has low exposure dose. Test results are digitalized, so it is available to compare to other examinations. (It is favorable to women aged more that 40) |
It has low possibilities in discerning disease in the cases of women under 30s. It may be difficult to get results from dense breast. |
| Mammary Gland Ultrasonography | It is favorable for precise diagnosis of localized lesion. It is highly effective on detecting benign tumors from young women in their childbearing years. |
Results may be different depend on who perform. However, it is highly favorable for young women in their childbearing ages. |
|
| Colon cancer | CEA(Carcinoembryonic antigen) test | It is simple blood test, which is used to check recurrent status. | Reliability is low. Rates of false positive and false negative are high. |
| Colonography | It is favorable for checking the overall shape of large intestine or lesion. It is helpful for planning surgery. | Biopsy is impossible. | |
| Colonoscopy | Precise diagnosis is possible. Biopsy is possible. | It is very painful for patients and hard for the operators. There may be risks of perforation. |
|
| Endoscopic ultrasound | The tumors beneath submucous layer which cannot be seen by colonoscopy can be detected. | As endoscopic ultrasound device distribution rate is low and the operators are rare, it is difficult to get this test. |
|
| Cervical cancer | Pap smear | It is simple and cheap. | It has low reliability. (with high rate of false negative) |
| Thin prep test | It is simple and accurate. | It has lower rate of false negative that pap smear. | |
| Cone biopsy | It is accurate and show low rate of false negative. | It is an invasive test method. | |
| Lung cancer | Chest radiography | It is the most basic examination, which helps infer next step. | |
| Sputum smear | It is not helping a lot. | ||
| Chest CT scan | Accurate diagnosis is possible. Low-dose CT scanning is recommended. |
Must be careful for high radiation exposure dose. There may be problems to make patients undergo unnecessary tests. |
|
| Bronchoscopy | It is recommended to take this examination at a hospital where the full-time thoracic physician or surgeon is. Biopsy is possible. | The cost is high. Patients may feel pain and there may be risks. | |
| Esophageal cancer | Endoscopy | Accurate diagnosis and biopsy are possible. | Patients may feel pain. |
| esophagography | It is possible to see the overall outline of the tumors and to check the effects of the tumors on the digestive system. | It is simple. Patients must use contrast medium, which may cause diarrhea, etc. | |
| Esophagus endoscopic ultrasound | Checking tumors beneath submuchous layer is possible. | The cost is high. | |
| Bladder cancer | Urine smear | It has low reliability. | |
| Cystourethrography | Accurate examination is possible. | Patients may feel uncomfortable. | |
| Ultrasonography | It is possible to see the overall outline but not as good as Cytourethrography. It is useful for check tumors beneath submuchous layer. |
||
| Prostate cancer | DRE(Digital rectal examination) | It is simple and cheap. | It has high rate of false negative. |
| PSA test | It is a simple blood test. | It has high rate of false positive. | |
| Endorectal Ultrasound | It is the most accurate. | The cost is high. |
08
Integrative Cancer-immunotherapy
can be cured by the patient's own immunity.
Integrative cancer-immunotherapy is a patient-centered treatment method which utilizes the patient's immunity as much as possible for curing and recovering from cancer.

Integrative cocktail cancer-immunotherapy is the fundamental treatment method.
Performing surgery, radiation, anti-cancer drug regimen without restoring immunity may raise possibility of recurrence, that is because cancer cells are developed by declining of immunity. Restoring immunity is the fundamental cancer treatment method. Therefore, it is more effective when immunotheratpy is performed with modern medical treatment such as surgery, radiation, anti-cancer drug regimen, etc.· Immunotherapy
· Modern Medical Treatment, Radiation
· Modern Medical Treatment, Surgery
· Modern Medical Treatment, Anti-cancer Drugs
Constant integrative cocktail cancer-immunotherapy have positive effects on cancer prevention on
precancerous stage, and maximization of the remedial value and recurrence prevention after cancer developed.
In case of recurrence even after anti-cancer drugs regimen and radiotherapy performed, because cancer cells become resistant to those treatments, it is difficult to be improved by anti-cancer drugs or radiation. Integrative immunotherapy inhibits carcinogenesis stage by restraining cancer cell production mechanism on precancerous stage, and helps revitalize immune cells and prevent cancerization environment after cancer developed.




